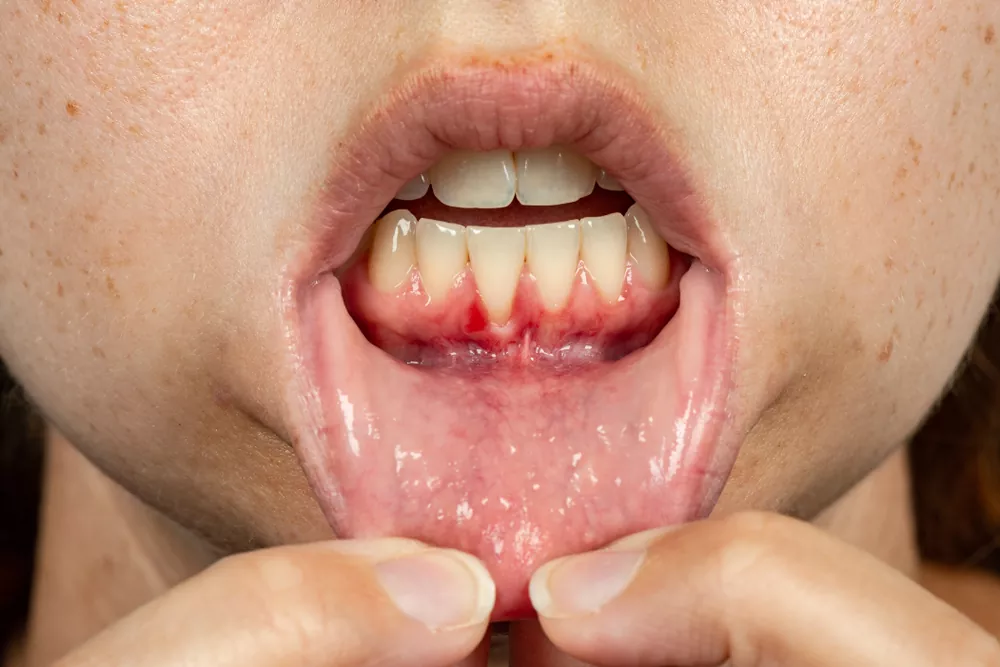
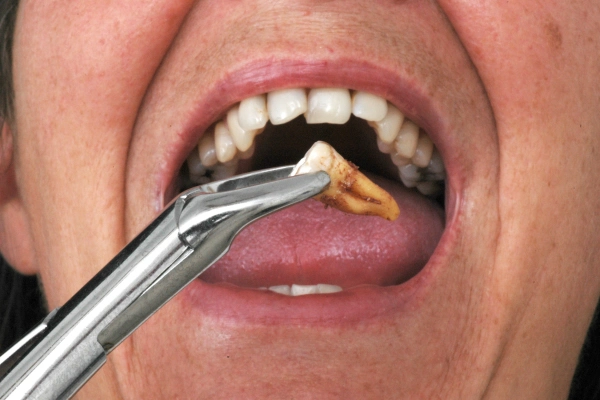
Gums are like the foundation of a building — strong, supportive, and mostly hidden. But when they begin to pull back or recede, they expose the tooth’s roots, leading to sensitivity, infections, and — in extreme cases — tooth loss. So, how far can gums recede before teeth fall out? The short answer: When enough gum and bone support is lost, the tooth becomes unstable and can eventually fall out or require extraction.
But there’s more to understand. In this article, we’ll explain:
- What gum recession really is
- The stages of gum recession
- At what point teeth become loose or fall out
- Signs to watch for
- Treatment options before it’s too late
Let’s dig deeper — before your gums shrink any further.
What Is Gum Recession?
Gum recession is the process where the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or its root.
It’s often a symptom of underlying gum disease, but it can also result from poor brushing habits, smoking, hormonal changes, or genetics.
Why Gums Matter for Tooth Stability
Gums protect the periodontal ligament and the alveolar bone — two structures critical for holding your teeth in place. As the gums recede, these underlying supports may also begin to deteriorate. The longer the root is exposed, the more vulnerable it becomes to:
- Decay
- Bacterial infections
- Bone loss
- Tooth mobility
How Far Can Gums Recede Before Teeth Fall Out?
There isn’t a specific “millimeter” at which a tooth will fall out. But research and clinical observation suggest:
- 1–2 mm of gum recession: Mild stage, usually manageable with good hygiene and professional care.
- 3–4 mm: Moderate recession. The tooth may become sensitive or prone to decay but is still stable.
- 5+ mm: Severe recession. At this point, the bone may also be compromised, and the tooth can become loose.
- Beyond 7 mm: Often a sign of advanced periodontitis, where both gum and bone support are severely diminished. This is the danger zone — teeth may fall out or need extraction.
🦷 Key point: Teeth don’t fall out because of gum loss alone — it’s the combined loss of gum tissue and bone that makes a tooth unstable.
What Causes Gum Recession?
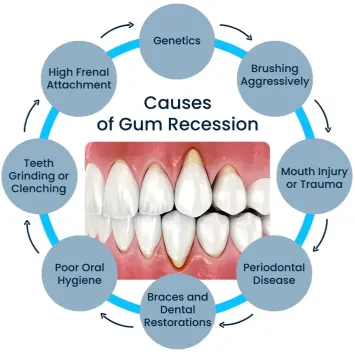
Here are the most common triggers that lead gums to retreat:
1. Periodontal (Gum) Disease
This is the #1 cause. Bacterial plaque inflames and destroys the gum and bone tissue over time.
2. Aggressive Brushing
Brushing too hard with a stiff toothbrush can literally scrub your gums away.
3. Smoking and Tobacco Use
Tobacco restricts blood flow, weakens tissue, and contributes to gum deterioration.
4. Genetics
Up to 30% of people may be genetically predisposed to gum issues, even with good oral hygiene.
5. Hormonal Fluctuations
Pregnancy, menopause, or other hormonal shifts can make gums more vulnerable.
6. Poor Dental Care
Not flossing or brushing properly allows plaque and tartar to build up, triggering inflammation.
Learn more here: https://dentistdecode.com/gums-recede-before-teeth-fall/
How Do You Know If Your Gums Are Receding?
Here are early and late-stage signs to watch for:
🚩 Early Symptoms:
- Tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet
- Gums look thinner or more “stretched”
- Teeth appear longer
- Notching near the gum line
🚨 Advanced Warning Signs:
- Loose or wobbly teeth
- Pus or discharge near the gum line
- Persistent bad breath
- Gums that bleed easily
- Deep “pockets” between teeth and gums
If you’re noticing any of these, especially tooth mobility, it’s time for immediate intervention.
When Is It Too Late to Save the Tooth?
If a tooth has severe mobility, 7+ mm gum pockets, and extensive bone loss, saving it becomes increasingly difficult. However, modern dentistry offers some hope. Your periodontist may still try:
- Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing)
- Laser therapy
- Bone grafting
- Soft tissue (gum) grafts
- Regenerative procedures
- Tooth splinting for stabilization
👉 If these treatments fail and the tooth becomes too unstable, extraction may be the only option.
Can Teeth Fall Out from Gum Recession Alone?
Technically, gum recession alone doesn’t cause teeth to fall out — but it sets the stage for tooth loss. As more root surface becomes exposed, bacteria find a pathway to the bone, causing it to degrade.
Once the supporting bone is gone, the tooth has nothing to hold it in place.
Can You Reverse Gum Recession?
Here’s the honest answer: Gum tissue doesn’t grow back naturally once lost. However, you can:
- Stop further progression through proper hygiene and care
- Regrow lost support with advanced dental treatments
- Cover exposed roots with surgical grafts
Early detection is the key.
Treatment Options for Gum Recession
🪥 1. Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
Removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooths the root surface.
🩸 2. Gum Grafting
Transplants healthy tissue (usually from the roof of the mouth) to the affected site.
🔬 3. LANAP (Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure)
A laser therapy that removes diseased tissue and helps regenerate bone and ligaments.
🦴 4. Bone Grafting
Used when recession has affected the jawbone.
🦷 5. Tooth Splinting
Connects loose teeth to nearby stable ones for support.
How to Prevent Further Gum Loss
- Use a soft-bristle toothbrush and gentle circular strokes
- Floss daily (properly)
- Avoid tobacco in all forms
- Get regular dental cleanings
- Manage conditions like diabetes
- Use desensitizing toothpaste if roots are exposed
- Treat bruxism (grinding) if present — it worsens gum recession
FAQs About Gum Recession and Tooth Loss
Q: How long does it take for teeth to fall out from gum recession?
A: It varies. For aggressive periodontitis, it can happen in a few years. In milder cases, it may take decades or never happen if treated early.
Q: Can I fix gum recession without surgery?
A: Mild cases can be managed with deep cleaning and good oral hygiene. Severe cases typically require surgical grafts.
Q: Is tooth loss from gum recession common?
A: Yes. Gum disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults over 30.
Final Thoughts: Take Gum Recession Seriously
So, how far can gums recede before teeth fall out?
The answer isn’t about a magic number — it’s about how much bone and gum support you lose before the tooth becomes unstable. When gum pockets deepen to 6–7 mm or more, and bone loss is evident, tooth loss becomes a real risk.
But here’s the good news: Gum recession is treatable and manageable, especially when caught early. With modern treatments, good hygiene, and regular dental care, you can protect your smile for life.Don’t wait until your tooth is loose. If you notice signs of gum recession, schedule a dental checkup — and save your smile before it’s too late.